Functions in Excel are many and are divided into categories based on their functions such as database functions, information functions, technical functions, etc. In which there will be 10 functions that we often use in Excel. like the SUM function in Excel, the IF function, or the DAYS function.
The DAYS function belongs to the group of date functions, used to return results between two dates. With this DAYS function, the calculation of time periods will be much easier, which can be applied to many different cases. The following article will guide you how to use the DAYS function in Excel.
Instructions for using the DAYS function in Excel
The DAYS function in Excel has a syntax to use = DAYS(end_date, start_date).
In there:
- end_date: the end date you want to specify the number of days, is a required parameter.
- start_date: the first date you want to determine the number of days, is a required parameter.
Note when using the DAYS function:
- If end_date and start_date are both numeric, the function uses EndDate – StartDate to calculate the number of days between these two dates.
- If one of the end_date and start_date values is in text, the function automatically converts to the date format using the DATEVALUE(date_text) function and then calculates.
- If end_date and start_date are outside the range of valid dates, the function returns the #NUM! error value.
- If the text argument cannot be converted to a valid date format, the function returns the #VALUE! error value.
Example 1: Calculate the time distance
We have the time table below with different timelines and formats.
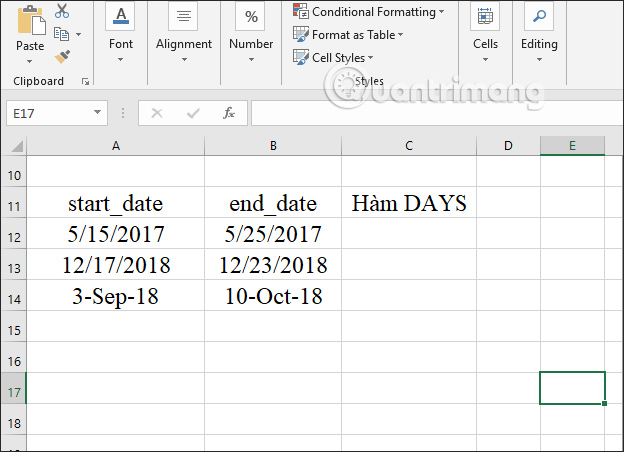
In the first cell to enter the time distance calculation result, we enter the formula =DAYS(B12,A12) and press Enter.
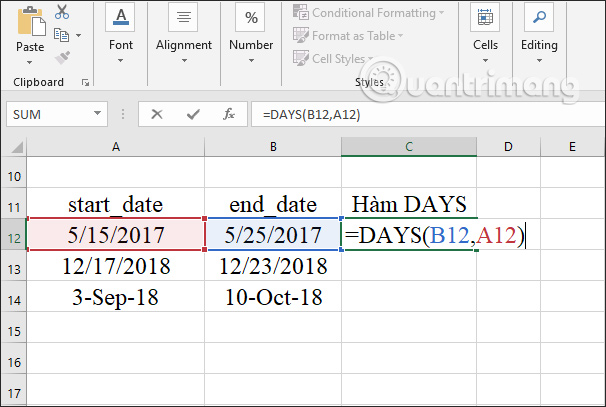
As a result, we get the time distance between 2 different time points. You drag the first result cell down to the rest of the table cells.
Example 2: Calculate the number of years of service of the employee
To calculate the number of years of service for an employee, the user must use the DAYS function to calculate the working time and then divide by 365 to get the number of working years.
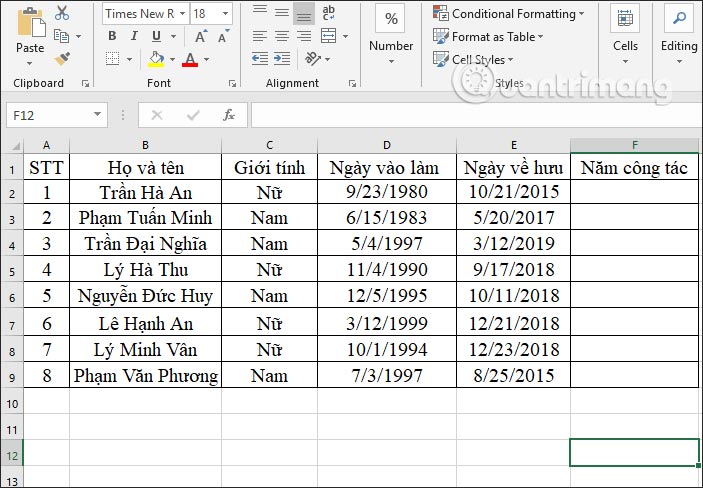
Step 1:
In the first working year cell, we enter the calculation formula =DAYS(E2,D2)/365 and press Enter.
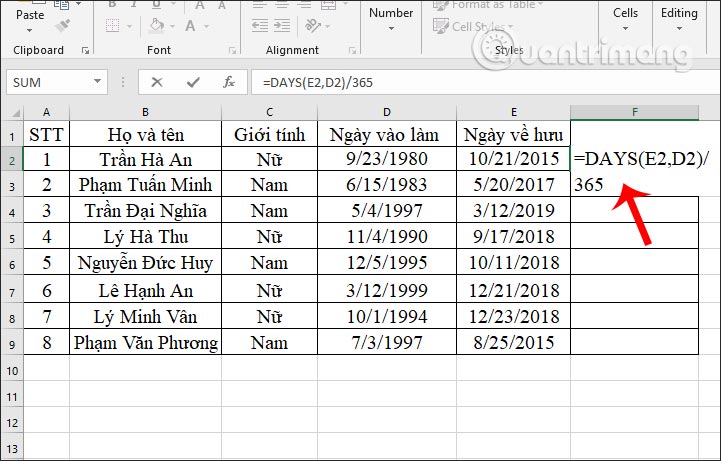
Step 2:
When you display the first result, drag down the remaining cells.
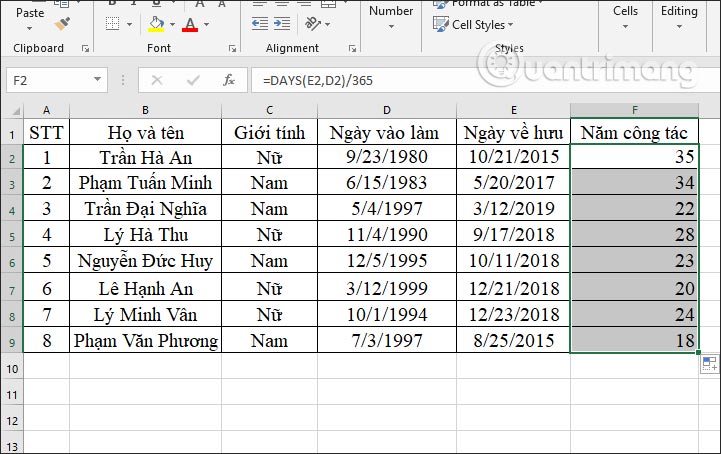
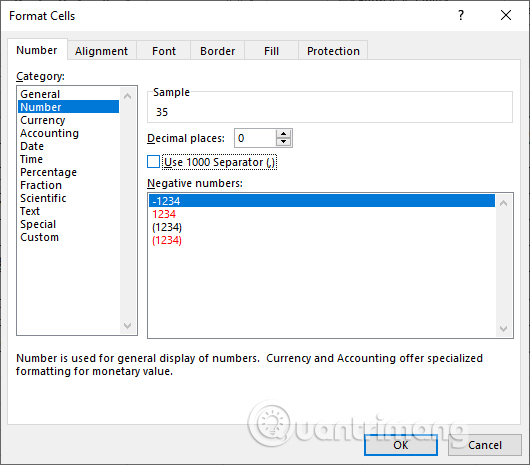
Note if the results do not display the number of years, then right-click and select Format Cells. Then we choose the Number format. If the result displays decimals, remove the product at Use 1000 Separator and then enter 0 at Decimal palces to display the integer value for the number of years.
In case someone has not retired, we have to enter another formula to calculate the number of years of service up to the current time, enter the data.
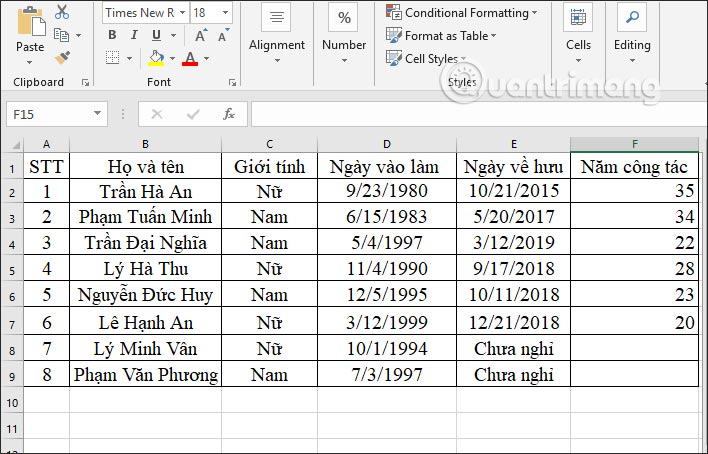
In the input box, we enter the formula =DAYS(TODAY(),D8)/365 and press Enter. In which cell D8 will be the starting time to calculate the working seniority until the current year.
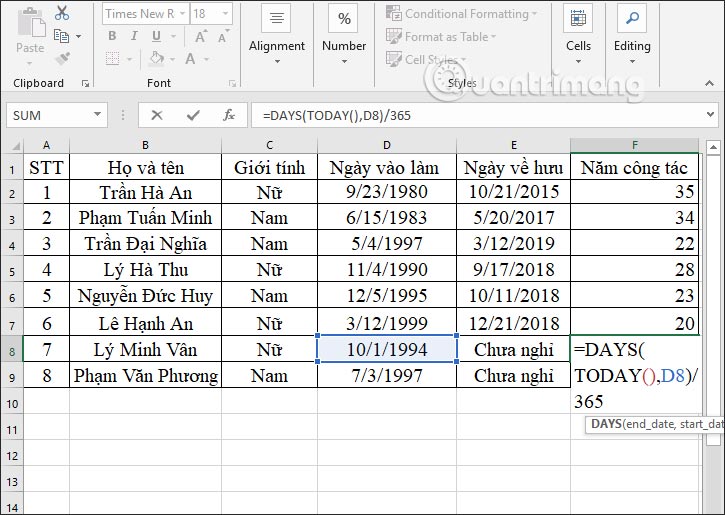
The results display and calculate the number of years of service to the current year. You drag down the remaining cell to display the results.
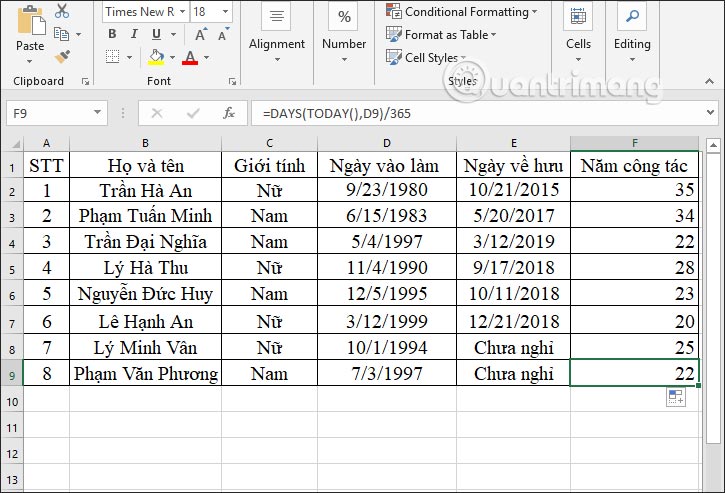
Above are some examples for the DAYS function in Excel. Often, the DAYS function will be combined with other functions such as the TODAY function to calculate a certain time period.
Wishing you success!
Source link: DAYS function, how to use the function to calculate the number of days between two dates in Excel
– https://techtipsnreview.com/






