Everyone uses wifi. It’s a fact of modern life, but it comes with some serious security risks. A home wireless network is possibly the most insecure Internet connection. You can be attacked from the Internet and even from your neighbors.
While no security measure is perfect, there are some simple steps you can take to enhance the security of your home wireless network and make it harder for attackers to gain access.
Always access the admin console using Ethernet
Logging into the router’s admin console is as simple as opening a web browser, entering the IP address (or sometimes the URL), and then the router admin username and password. Everything is fine, as long as you don’t do so on a wireless connection.
When logging into the admin panel over the air, those logins are sent over the network and potentially intercepted in the middle. If you only log in when connected by Ethernet, you can eliminate this risk.
In fact, you should disable remote access entirely and require a wired connection to tune things up. This way, even if hackers tamper with your wireless connection and break your password, they won’t be able to change anything.
Change network name (SSID)

This is a very simple measure, change the default network name. The attacker knows the default name used by router manufacturers and ISPs. If they could figure out what type of router you’re using just by looking at your network name and be able to attack the exact router that’s much easier. It saves them both time and effort.
Plus, this kind of information opens the door to more sophisticated attacks that attack router-specific firmware. An attacker can directly exploit the firmware and gain more access and in a more discreet way if they just find out your password.
Change username and password
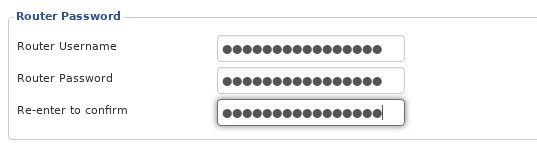
Similar to the security method above, you need to change the username and password of the network administrator user.
Attackers know the default username and password, and they try those first. Don’t think you’re smart just by changing your password or changing one character. An attacker has a tool that can quickly test thousands of username and password combinations.
Change the admin username to something a bit unpredictable. The password must be a passphrase. That means it must be a phrase containing at least one or more meaningless words. You should also use capital letters, numbers, and a few special characters.
Change the router’s default IP address
For security reasons, it’s best to change your router’s default IP (the IP address you enter in your browser to connect to the router), making it more resistant to tracking.
1. While logged in as admin, look for the option Network Configuration or something similar.
2. Change one or both of the last numbers of the IP address in the field LAN IP Address. For example, you can change the default IP to 192.168.200.01 on my router to 192.168.200.36 (the actual IP address on your router will be different).
3. Click Apply or Save and wait for your router to reboot.
Use strong encryption
Encryption is a must-have feature on all routers. Bypassing encryption is like leaving all the doors and windows open in your home. Everything you say or do can be seen and heard by anyone.
If you’re not using encryption for your wireless network, you’ve made a big mistake. In fact, if you are using encryption, you can still make mistakes. Not all encryption is created equal. Make sure you have selected the correct setting.
Seriously, it only takes about 30 seconds to enable encryption in the router settings. And in doing so, make sure you use WPA2 mode if it’s available, or use WPA Personal. Don’t use WEP encryption anyway, as it’s weak and easy to crack.
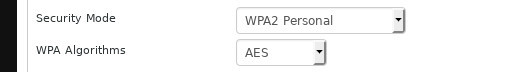
Choose “WPA2 Personal” for your network. It would be nice if you could set up the enterprise version, but it’s really not that easy unless you already have some experience with it.
For encryption algorithm, choose AES, do not use TKIP. AES provides stronger encryption and is very difficult to exploit. TKIP was selected only as an option for backward compatibility, and if you really need TKIP, update your device.
Choose a strong password
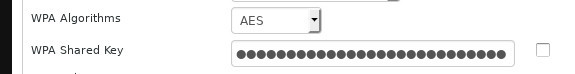
The password that you use to log into the network also needs to be strong and it needs to be different from the password for the administrator account. Choose a long password that includes at least one rarely used word, number, and special characters. Your password must be at least fifteen characters long.
Change WiFi password
Even if your Wi-Fi password is extremely strong, you need to change it. Like any password, you should regularly change it to new phrases. That doesn’t mean you need to change your password every day, but every few months is a good idea.
Set up DHCP Reservation settings (static IP address)
For most networks, the router can be kept at the default DHCP settings. This means that the router will automatically provide IP addresses to clients connected to the network, thus eliminating the work of IP management.
If you plan to connect a server or any device you can access from outside your network, the best option is to configure the settings DHCP Reservation. This simply means that you are telling the router that a particular device always uses a specific static IP address, which is reserved for it.
For example, the router’s IP address could be 192.168.1.1. So you can give your email server an IP address of 192.168.1.2. You can also give a third device, such as a web server, an IP address that is 192.168.1.3, etc..
Disable guest network
Guest networking can be a double-edged sword. Make sure your guests don’t log in and access your entire network, and they don’t use your password. However, if the guest network doesn’t have a password, you’re still open to anyone who wants to connect. You are essentially giving the attacker a chance to gain access to your network.
The only exception here is if you can create a separate password for the guest network. If your guest network has the same level of security as the main network, that’s fine. Otherwise, disable it and if you don’t trust your guests, change the password when they leave.
Turn on the firewall
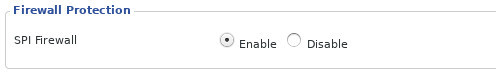
Not every router has a built-in firewall, but if yours does, enable it. Firewalls can act as your first line of defense. They are specifically designed to manage and filter traffic in and out of your network and can block access through unused ports.
Use VPN
You won’t prevent your neighbors from breaking into your network with a VPN, but you can prevent attacks from outside the nearest area that way.
When using a VPN, first connect to the VPN server, then connect to the external Internet. All traffic comes from the VPN, including any information about your internal computer network because VPNs create virtual intranets. While connected to them, your computer is on both a physical intranet and a virtual one. The Internet can only see the virtual network.
VPNs have the added benefit of anonymizing part of your traffic. A VPN won’t make you completely anonymous online, but it certainly helps.

WPS stands for Wifi Protected Setup. This is a system that connects to an encrypted wifi network without entering a password. There are some differences, but they’re all pretty much the same.
While WPS might work well in theory, it’s not really that good in practice. WPS can cause a number of security holes. It is enabled by default on most routers. If you feel you don’t need WPS, you can disable it and close these security holes.
Manage router firmware
Like computers, routers have an operating system. However, it does not automatically update security updates like a computer, so you need to update it yourself. Some routers can download firmware updates from the Internet. For other routers, you have to manually download them and upload them to the router from your computer.
Like with computers, updates often include important security fixes. If you don’t update, attackers will take advantage of these security flaws to attack you. You don’t have to do this often, just check for updates every month or so.
If you’re a little tech-savvy, you might consider using a custom open source router firmware. There are a few really great tools you can load up on your router, and it’s usually fast updates and more features. If you’ve never done this before, be careful as you could destroy the router.
Turn off remote management/unnecessary services
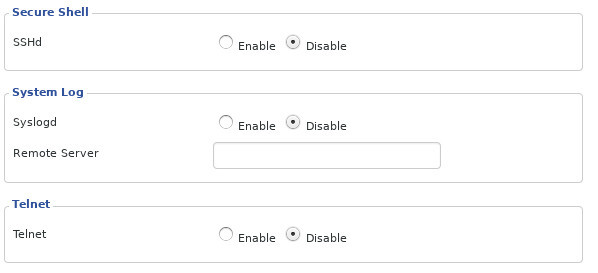
Many routers have remote management services. In some routers, these services are enabled by default. Don’t get confused here. This is not the web interface you use to manage the router from within the network, the remote services allow you to manage it from the outside. That means an attacker from the open Internet can gain access to your router’s management interface. There aren’t many practical reasons why you would need to manage your router from outside the network, so you won’t miss much by turning off this potentially dangerous service.
There are other services for which the router comes with it that is not necessary. For example, some routers come with SSH or Telnet enabled by default. There’s no reason at all, especially since you can use the router’s web interface. Some routers even have FTP and Samba enabled by default for file sharing. Both can make it easier for a cyber attacker. If you have them, turn them off.
MAC address filtering
All devices have a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address, which is used to communicate with a network segment.
By filtering the MAC address of each device, you can increase the security of your network. You can do this by adding the MAC addresses for all your devices to your wireless router preferences, ensuring that only filtered devices can make connections to the network.
You can usually find the MAC address in the menu Network Settings on your device, or by going to Command Prompt, type “getmac” and press Enter. The result will be similar to the following:
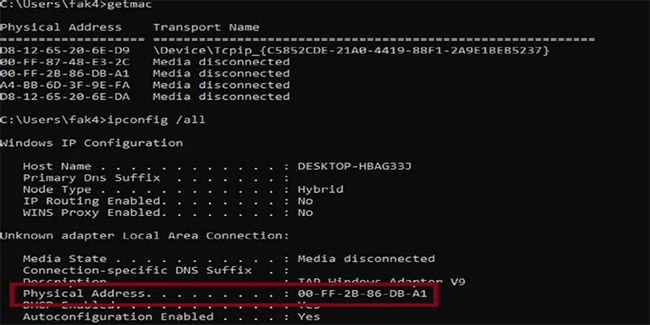
1. While logged into the router, look for the option MAC Filtering and click it. Option MAC Filtering can be listed as MAC Filter, Network Filter, Network Access, Access Control or something similar. It may be in the menu Wireless, Security or Advanced.
2. Click option to add MAC Filter new. The button will most likely be an icon that says “Add” or the plus sign (+) or something like that.
3. Enter the MAC address of each device in the network that you want to filter out.
If you are interested in the topic of security or you have read an article like this before, you may be wondering why some things are not covered. A good question! Static IP addresses, MAC filtering, and SSID hiding are all ignored as they have been proven not to work. Sure, you can prevent some minor interventions, but with the right tools, none of these tricks work. You should invest your time and efforts when it achieves results like encryption and strong passwords.
Be smart and do your best to make sure your router is protecting you.
Source link: How to secure the wireless network in your home
– https://techtipsnreview.com/





