Network Administration – In the article below, we will introduce and guide you to learn about the concept of QoS – Quality of Service on router devices.
What is QoS?
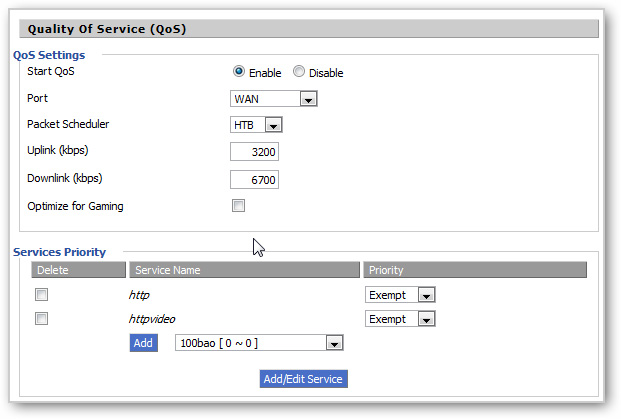
QoS (short for Quality of Service), is a way to control the traffic priority of the network, this feature works on all different layers of the system, but in this test, we will focus on router equipment used in home or personal models. More specifically, QoS will clearly show its effect in places where bottlenecks often occur (often called bottlenecks), and at the same time decide which traffic is more important than the rest, based on on the rules that the user establishes related to IP addresses, MACs, active services …
Where to use QoS in practice
For a little more understanding, let’s take the example of highway traffic congestion during rush hour. All drivers on the road have a goal of reaching their final destination. And so, they had to keep on moving, albeit at a snail’s speed.
Then, the sound of the ambulance horn alerted them to a vehicle that needed to reach their destination urgently and had to go ahead of them. As a result, the drivers move out of the way – now becoming the “priority road” of the ambulance and let it pass.
Similarly, when a network transmits data, it also has a setting in which some types of data are processed better than all others. Critical data packets need to reach their destination much faster than the rest, because they are time sensitive and will “expire” if they do not arrive on time.
Why is QoS important?
In the old days, the information network and the enterprise network were separate entities. Phone calls and remote communications are typically handled by a connected RJ11 network. The calls are monitored by a PABX system. It runs separately from the RJ45 connected IP network linking laptops, desktops, and servers. These two types of networks rarely intersect unless, for example, a computer needs a phone line to connect to the Internet. An example of such a network would look like this:
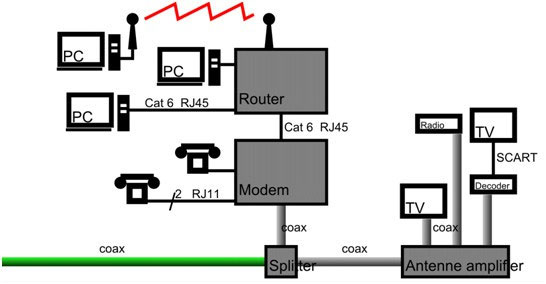
When the network only transmits data, speed doesn’t matter. Today, interactive applications that carry audio and video must be delivered over the network at high speed, so that there is no loss of data packets or changes in delivery speed.
People now make work calls using online meeting applications such as Skype, Zoom, and GoToMeeting, which use the IP transport protocol to send and receive video or audio messages. For the sake of speed, these critical applications can get the job done without the need for the management processes commonly used by standard data transfers.
Where does Bottleneck usually happen?
The main mechanism of action QoS often applied when the phenomenon bottleneck happens at a time or somewhere in the system, and the main factor here is the parameters you set are related to bandwidth:
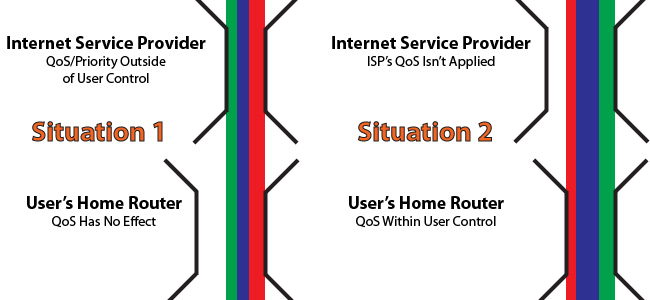
Assume that the settings of QoS is over-initialized bandwidth you received from your supplier. What will happen if the amount traffic on router Your system does not take priority because the system “thinks” that traffic bandwidth This is perfectly reasonable. Meanwhile, if you have used up to the limit of ISP’s provision, it is they who decide what is allowed and not allowed to continue operating.
Besides, if the bandwidth level setting of QoS is lower than the standard of the ISP, it means that you are creating an “artificial” bottleneck, and we can control, monitor and monitor them through router.
Some points to note to ensure stability in the system, including the setting of Uplink and Downlink:

Let’s start by checking the average speed we are using from our ISP. To do this, you can use some online support services available such as Speakeasy Speed Test and SpeedTest:

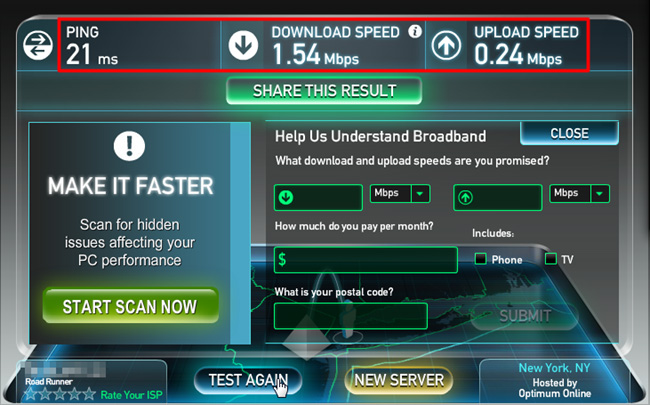
As recommended by experts as well as many experienced users, you should set up QoS with about 85% value obtained from testing to ensure that the system is working properly. After determining the speed Uplink and Downlink Gradually increase the interval twelfth% on every time. For some special cases the user can increase it 95% but the system still ensures performance, not affected by any side effects.
What if QoS is not used in the network?
Not having a correctly configured QoS can lead to one (or all) of the following problems:
Latency
When RTP packets have not been assigned the required priority, they are delivered at the device’s default speed. In a congested network, packets must travel with the rest of the non-emergency packets. Although the network delay itself will not affect the quality of the audiovisual data delivered, it will affect the communication between the end users. At 100ms latency, one person will begin to override another when incoming packets are out of sync and at 300ms, the conversation will be incomprehensible.
Jitter
Real-time applications eliminate standard transfer-level buffering, so there is no mechanism to reassemble incoming packets in the correct order. Jitter is the abnormal speed of packets on the network. It can lead to late and out of sequence packets. Because the application does not wait for the stream to be correctly arranged, out-of-order packets are skipped, resulting in distortion or gaps in the delivered audio or video.
Packet loss
This is the worst case scenario to find that some (or partial) packets are lost due to too much congestion on network devices. When the output queue of a switch or router is full, a Tail Drop occurs when the device rejects any new incoming packets until space is restored.
In all of the cases you’ve just seen, QoS can help with data sorting, queue management, and data loss prevention.
It’s not hard to imagine how seriously impacted communication and media streaming or streaming can be affected without using QoS – especially on networks that serve the RTP protocol. Even if it is perfectly designed, it eventually becomes difficult to communicate first, then deteriorates as network traffic increases, and ultimately becomes impossible.
These 3 errors are, in fact, very important in determining the quality of RTP-based traffic that QoS and network monitoring software companies such as SolarWinds use as metrics.
Network tool for monitoring QoS
SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer (Free Trial)
It would be quite unfair to go on without mentioning a bit more about one of the best network monitoring tools available: SolarWinds NetFlow Traffic Analyzer.
This network monitoring suite helps to solve problems that could be caused by:
– Slow network: A slow network can affect the business as it continues to slow data transmission rates. Unless the bottlenecks of the network are removed, the entire organization will experience poor connectivity.
– The communication process is slow: An enterprise that cannot establish a clear communication channel in its network is paralyzed. Worse yet, not being able to communicate clearly with customers will almost certainly cause business problems.
– The network is not monitored: Administrators who cannot properly monitor the network will not be able to know the current state of the network or how to plan for future network expansion. Without monitoring the network and monitoring the performance of each device, the network manager cannot make an informed decision and potentially exacerbate network performance issues.
Equipped with Netflow Traffic Analyzer, the network administrator will be able to solve common problems encountered, as this tool helps:
- Help implement QoS and optimize it – through data stream response
- Review and report on current QoS policy configuration, informing design decisions.
- Monitor bandwidth usage to determine which apps and devices are taking up network resources – these apps and devices can be isolated, rescheduled, or turned off.
The Netflow Traffic Analyzer dashboard typically contains the important information an administrator needs to monitor status and make quick setting adjustments. An example:
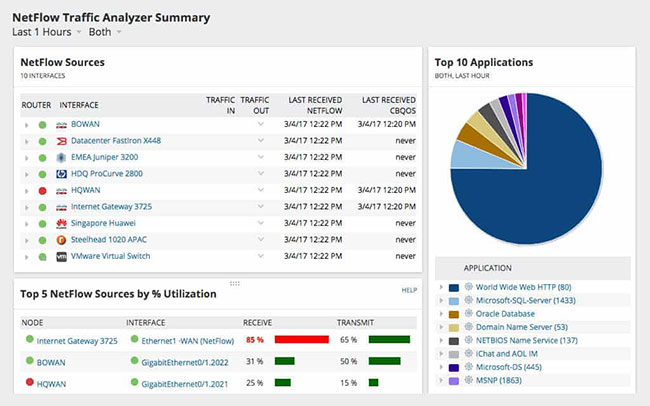
These reports and analyzes include: Latency, Jitter, and packet loss.
Paessler PRTG
Another option you can use for QoS monitoring is the Paessler PRTG. This network monitoring toolkit has a special section that monitors QoS performance. This function shows you tagged traffic streams in real time, and it also stores data for performance analysis and capacity planning.
PRTG software includes 4 monitoring sensors, including 3 different QoS methods. They add a Ping Jitter sensor that monitors the regularity of packet delivery in a stream.
The three types of QoS that PRTG can monitor are Standard QoS, Cisco IP-SLA, and Cisco CBQoS. The standard QoS tracker is applied either as a one-way sensor or a Round Trip sensor. These trackers can work over connections throughout the Internet.
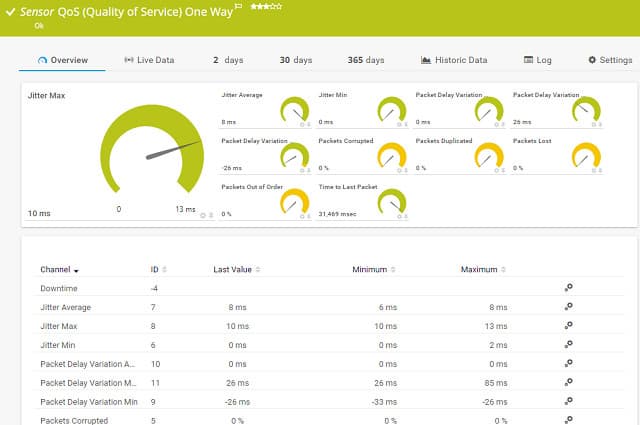
Cisco IP-SLA sensors are dedicated to monitoring tagged VoIP traffic on your network. It records a wide range of metrics for voice traffic, including lap time delay, latency, Jitter and Mean Opinion Score (MOS).
Cisco CBQoS sensors follow a layer-based implementation of Quality of Service. CBQoS is a queuing method and if you want to deploy it, you will have to keep track of multiple entries on your routers and switches. You create at least 3 virtual queues per device, so there’s a lot more to keep track of.
PRTG can automatically set up and map all of your network infrastructure. However, implementing QoS requires decision-making, so you’ll have to set the method yourself by deciding what type of network traffic to prioritize.
Paessler lets you use PRTG for free if you only have up to 100 sensors activated. If you need more, you can try the system for free for 30 days, including QoS monitoring.
Good luck!
Source link: What is QoS? How to use QoS to get faster Internet speed when urgent
– https://techtipsnreview.com/





