[*]
Comeinand net use is the Command Prompt command used to connect, delete, and configure connections with shared resources, such as mapped drives and network printers.
It is one of many net commands such as net send, net time, net user, net view, etc.
Availability of the net use command
This command is available in the Command Prompt on Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP, as well as in earlier versions of Windows and in the Windows Server operating system.
Recovery Console, the offline repair utility in Windows XP, also includes the net use command, but you cannot use it in the tool.
Note: The availability of certain switch and other command syntax may vary between operating systems.
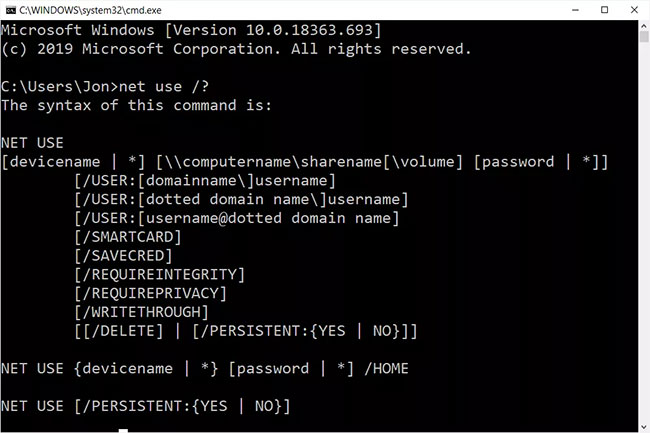
The syntax of the net use command
This command uses the following general syntax:
net use [{devicename | *}] [\computernamesharename[volume] [{password | *}]] [/user:[domainname]username] [/user:[dotteddomainname]username] [/user:[username@dotteddomainname] [/home {devicename | *} [{password | *}]] [/persistent:{yes | no}] [/smartcard] [/savecred] [/delete] [/help] [/?]The net use command options:
| Option | Explain |
| net use | Execute only the net use command to display detailed information about the currently mapped drives and devices. |
| devicename | Use this option to specify the drive letter or printer port for which you want to map network resources. For a shared network folder, specify the drive letter D: come Z:, and with shared printers, LPT1: come LPT3:. Use * instead of specifying devicename to automatically assign the next available drive letter, starting with Z: and undo, for a mapped drive. |
| \ computername sharename | This specifies the name of the computer, computername, and shared resources, sharename, like a shared folder or a shared printer is connected to computername. If there is a space here, be sure to enclose the entire path, including the slash, in quotes. |
| volume | Use this option to specify volume when connected to NetWare server. The Client Service for NetWare or Gateway Service for Netware must be installed. |
| password | This is the password required to access the shared resource above computername. You can choose to enter the password while executing the net use command by typing * instead of the actual password. |
| / user | Use this net command option to specify one username to connect to resources. If you don’t use / user, net use will try to connect to the network share or printer using your current username. |
| domainname | Specify a different domain from the one you are currently using, assuming you are using a domain, with this option. Skip domainname if you are not on a domain or you want to use net use to use an existing domain. |
| username | Use this option with / user to specify the username to use to connect to the shared resource. |
| dotteddomainname | This option specifies the fully qualified domain where username existing. |
| / home | This net use command option maps the current user’s home directory to the drive letter devicename or the available drive letter followed by *. |
| / persistent:{ yes | no} | Use this option to control the stability of connections created using the net use command. Choose yes to automatically restore the connections created at the next login, or select no to limit the life of the connection for this session. You can shorten this switch to / p if you want. |
| / smartcard | This switch tells the net use command to use the credentials found on an existing smart card. |
| / savecred | This option stores password and information user For use the next time you connect during this session or in all future sessions when used with / persistent: yes. |
| / delete | This net use command is used to disconnect from the network. Use / delete with devicename to delete a specified connection or with * to delete all mapped drives and devices. This option can be shortened to / d. |
| / help | Use this option, or shorten it to /H, to display detailed help information for the net use command. Using this switch is like using the net help command with net use: net help use. |
| /? | The standard helper switch also works with the net use command but shows only the command syntax, without any details about the command options. |
An example of the net use command
Here are a few different ways you can use this command:
The drive is temporarily mapped
net use * "\servermy media" /persistent:noIn this example, the net use command is used to connect to the shared folder my media on the computer named server. Folder my media will be mapped to the highest available drive letter [*], in this example it’s y:, but don’t keep mapping this drive every time you log on to the computer [/persistent:no].
The drive is permanently mapped
net use e: \usrsvr002smithmark Ue345Ii /user:pdc01msmith2 /savecred /p:yesThe above is a slightly more complicated example that you might see in a business environment.
In this net use command example, I want to map my e: drive to the shared folder smithmark on usrsvr002. The author wants to connect as an existing user account [/user] by name msmith2 is hosted on the domain pdc01 where the password is Ue345Ii. I don’t want to manually map this drive every time I start the computer [/p:yes], as well as do not want to enter username and password every time [/savecred].
List all shared resources
net useIn this simple net use command, you get a list of all shared resources currently in use under the logged in user account. In the example, the result in the Command Prompt shows “Z: \ server shared folder ” because z: is the drive letter you are connecting to shared folder on server.
The message “There are no entries in this list.” is displayed if no connections are currently established.
Unmapping a drive
net use p: /deleteThe last example of a net use is delete [/delete] the drive is currently mapped, in this case, p:.
Source link: How to use the Net Use command in Windows
– https://techtipsnreview.com/





